Active Directory (AD) Organizational Structure: Understanding AD Forests
- Domains
- Trees
- Forests
What is Active Directory?
To understand what a forest is, you must first understand Active Directory and its purpose. Active Directory (AD) is a database used to allow administrators to manage authentication of user accounts and authorize user access to network resources. Active Directory is based on the Light Weight Directory Protocol (LDAP) standard, which is a directory service installed on a Microsoft Windows server.
Active Directory data contains objects, which represent users, groups, contacts, and devices. These AD objects are categorized into object containers called organizational units (OUs), that look like folders. Objects and containers have unique security identifier (SID) and attributes such as Object Name, Department, City, and so on.
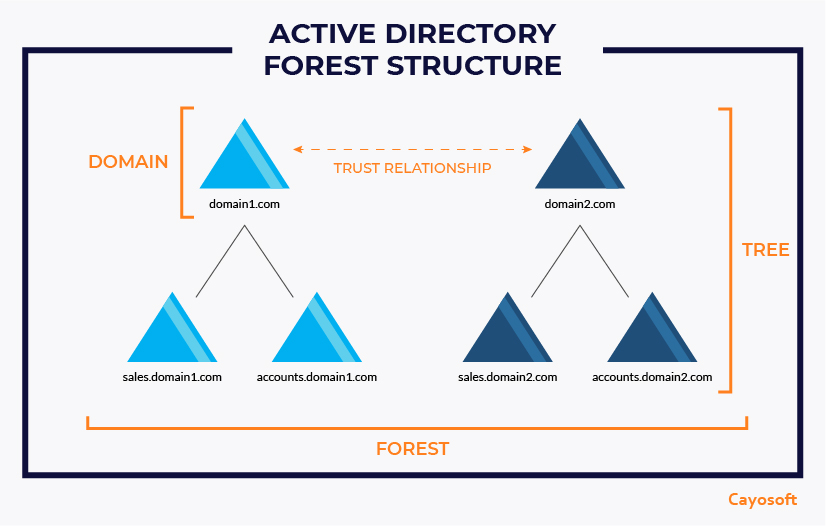
What is a Domain in Active Directory?
An Active Directory root domain, also referred to as a root, is where the Active Directory tree structure starts. It is the first domain at the top of the namespace and defines naming conventions used within the forest. It is the initial scope of authentication and the initial storage location of Active Directory objects.
What is a Tree in Active Directory?
What is a Forest in Active Directory?
A forest is the highest level of organization within Active Directory and is used to group one or multiple domains together. An Active Directory forest simply refers to all domains within a single AD installation and represents the security boundary of Active Directory. Forests allow administrators to assign broad policies, while trees and individual domains allow for more granularity in access and security.
Enterprise networks can hold hundreds of users and individual trees, which can have one or more domains or subdomains starting from the first setup domain, called the root domain. All together, these trees are organized into a forest, establishing a security boundary for network objects. It contains all the users, domains, devices, policies, and network objects in the hierarchy underneath.
The Active Directory Forest Model Structure
Forest Trusts
- Forest Trust: An Active Directory forest provides a security boundary to manage relationships for users to access resources. An Active Directory forest trust establishes a link between one or more forests to allow management of objects and resources across forest boundaries.
Active Directory Schema
- Active Directory Schema: The Active Directory schema defines the attributes that are applied against Active Directory objects and their classes.
Global Catalog
- Global Catalog: A global catalog allows the domain controller (DC) to provide information on each of the Active Directory objects within the forest. Global catalogs allow for faster searches across a forest because it contains reference information about all objects within each individual domain.
Organizational Forest Model
- Organizational Forest Model: In the organizational forest model, user accounts and resources are contained in the forest and managed independently.
This model is the simplest form and typically the standard configuration. The organizational model can be used to provide autonomy within the forest and isolate services or data from anyone outside the forest. Trust relationships can then be established making it possible for administrators to grant access to resources in the other forest.
Resource Forest Model
- Resource Forest Model: A resource forest model is where separate forests are created specifically for resources.
Restricted Access Model
- Restricted Access Forest Model: A restricted access model includes multiple separate forests with no trust relationships between them
Read our Active Directory Management Tools guide to learn more about managing Active Directory with native and third-party tools.
Active Directory Forest Best Practices
Active Directory forests are complicated, dynamic environments, leaving significant room for error and vulnerabilities ripe for attack. Microsoft provides some overall best practices for Active Directory, like managing a password policy, keeping track of inactive users, continuous monitoring, and regular housekeeping. We’ve also compiled a few to help you keep your Active Directory environment stable and secure.
Consolidate
It is best practice to consolidate multiple forests into a single forest, whenever possible. However, if you need an additional layer of security between two Active Directory domains, it may make sense to leverage multiple forests within Active Directory. Keep in mind, each forest you maintain requires additional management.
Active Directory forests can be linked together by establishing forest trusts, as mentioned above, which govern access permissions for user accounts that need access to both Active Directory forests.
Control and Restrict Access
Avoid the Empty Forest Root Domain
Track and Limit Admin Permissions, Resources, and Enforce Naming Conventions
It is easy to create a mess if you are not vigilant using consistent naming conventions for Active Directory objects. Administrators also need to be extremely careful assigning permissions, especially with nested groups based on parent-child hierarchy. It can be incredibly easy to assign permissions to a group that has nested privileges that provides access to areas that users should not have. Enforcement of naming conventions and permissions assignments is complex and will require the use of 3rd party solutions such as Cayosoft Administrator.
Secure
- Managing the potential threat vectors including typical breach targets, such as unpatched software, gaps in antivirus/antimalware, misconfigurations, privilege escalation, etc.
- Hardening systems against attack (physical access, domain controller operating systems, and secure configurations)
- Monitoring for potential attack vectors and unwanted changes
- Detailed planning for threat mitigation, business continuity, and disaster recovery
Want to learn more about ways to secure and recover your Active Directory forest?
Learn more about Cayosoft Guardian Forest Recovery, the only all-in-one solution for instantly recovering your Microsoft directories, or schedule a personalized demo to see how Cayosoft can help you ensure your identities recovered after ransomware strikes!