Home » Active Directory Management Tools: Must-Have Features » The Complete Guide to Active Directory Forests: From Planning to Implementation
The Complete Guide to Active Directory Forests: From Planning to Implementation
Learn about the importance of backing up Active Directory to ensure data consistency and protect against cyber threats, including best practices and key considerations for implementing an effective backup strategy.
Explore the chapters:
- Chapter
- Active Directory Management Tools
- Active Directory Group Policy Management
- Active Directory Security
- Active Directory Management
- Active Directory Disaster Recovery
- Active Directory Auditing
- Active Directory Groups
- Disable Active Directory
- Active Directory Reporting
- Active Directory Backup
- Active Directory Forests
- Active Directory Monitoring
- Chapter
- Active Directory Management Tools
- Active Directory Group Policy Management
- Active Directory Security
- Active Directory Management
- Active Directory Disaster Recovery
- Active Directory Auditing
- Active Directory Groups
- Disable Active Directory
- Active Directory Reporting
- Active Directory Backup
- Active Directory Forests
- Active Directory Monitoring
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
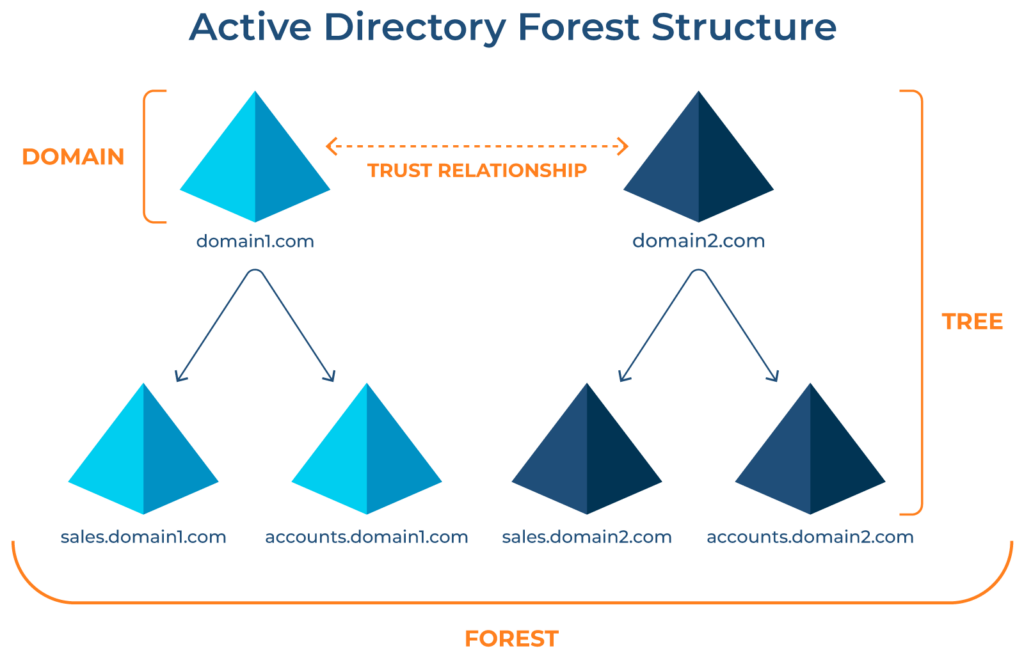
An Active Directory forest or AD forest is a fundamental AD concept. AD forests are hierarchical containers that contain and manage users, computers, group policies, and domains. It has multiple domains, each with a tree-like structure of users, computers, and relevant group policies. This secured layer provides greater isolation but can impose configuration and implementation challenges on IT administrators.
In this article, we’ll provide an in-depth overview of Active Directory forest, its key concepts, how to create one, and how Cayosoft can help manage, monitor, and protect your Microsoft AD environments on-premise and in the cloud.
Summary of Key of Active Directory forest concepts
The table below summarizes three essential active directory forest concepts this article will explore in more detail.
| Key Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Organizational forest model | Centralizing user accounts, groups, and resources within a single forest for unified management and streamlined administration. |
| Resource forest model | Isolating network resources such as servers, printers, and applications into dedicated forests to simplify management and enhance security. |
| Restricted access forest model | Enforcing strict security boundaries by creating multiple forests without trust relationships, limiting access to sensitive data and resources. |
Active Directory forest design models
AD forest design models allow you to manage users and resources according to organizational requirements. For this purpose, Microsoft introduced three AD forest models: organizational, resource, and restricted access design models. SMBs and large enterprises can use them according to their business needs. Let’s discuss each design model in a bit of detail:
Organization forest model
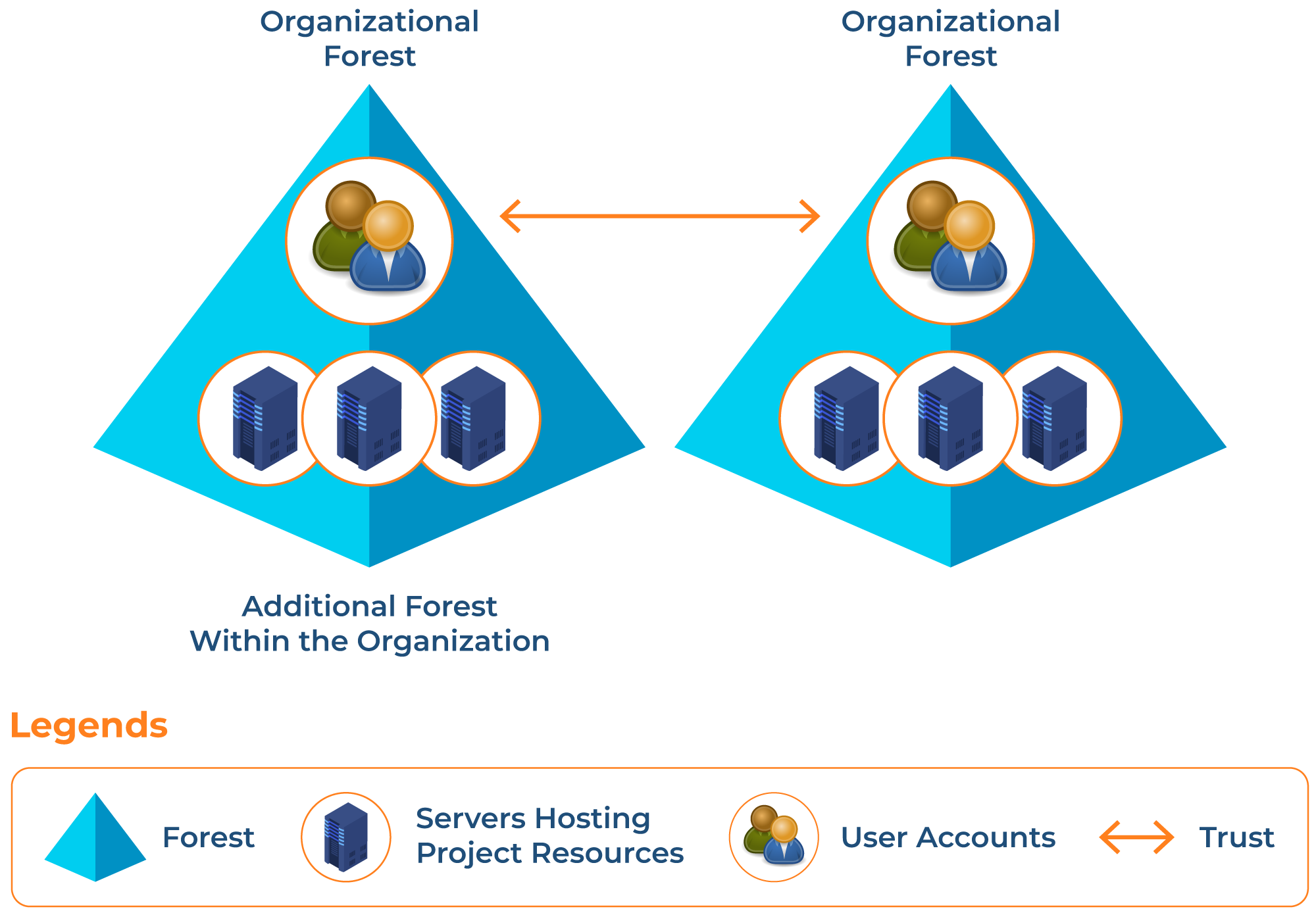
The organizational forest model allows you to manage users and groups independently and from a single forest. In this model, you manage your resources in isolation where no other resource can communicate outside this forest. Still, you can establish a relationship of trust with other forests. This allows system administrators to grant or deny access to users and groups in other forests.
Resource forest model
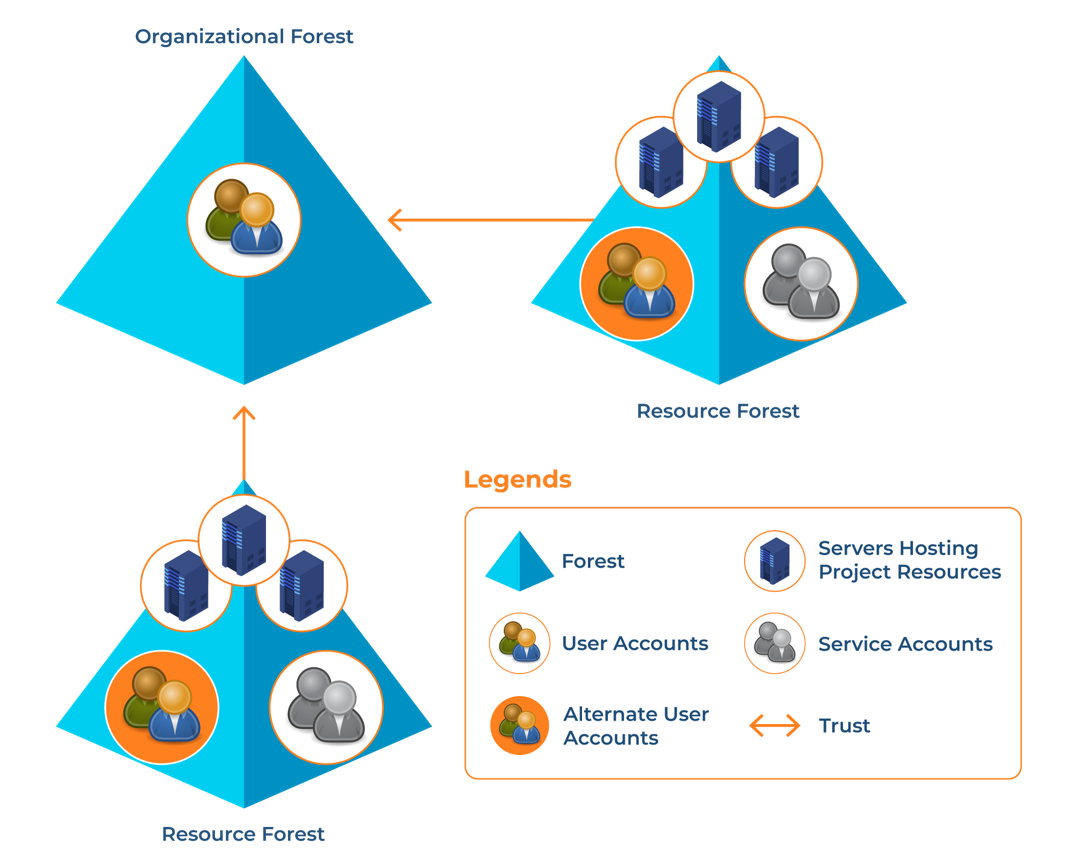
The resource forest model allows you to use a separate forest to manage AD resources. In this model, you don’t have any user accounts except for service administration and other accounts created for some other specific tasks. You can use these specific user accounts when user accounts are not available in the organizational forest.
It’s not commonly used, but you can use the resource forest model when service isolation is needed. This model protects specific areas of your network that need to manage high availability for critical applications and resources.
Restricted access forest model
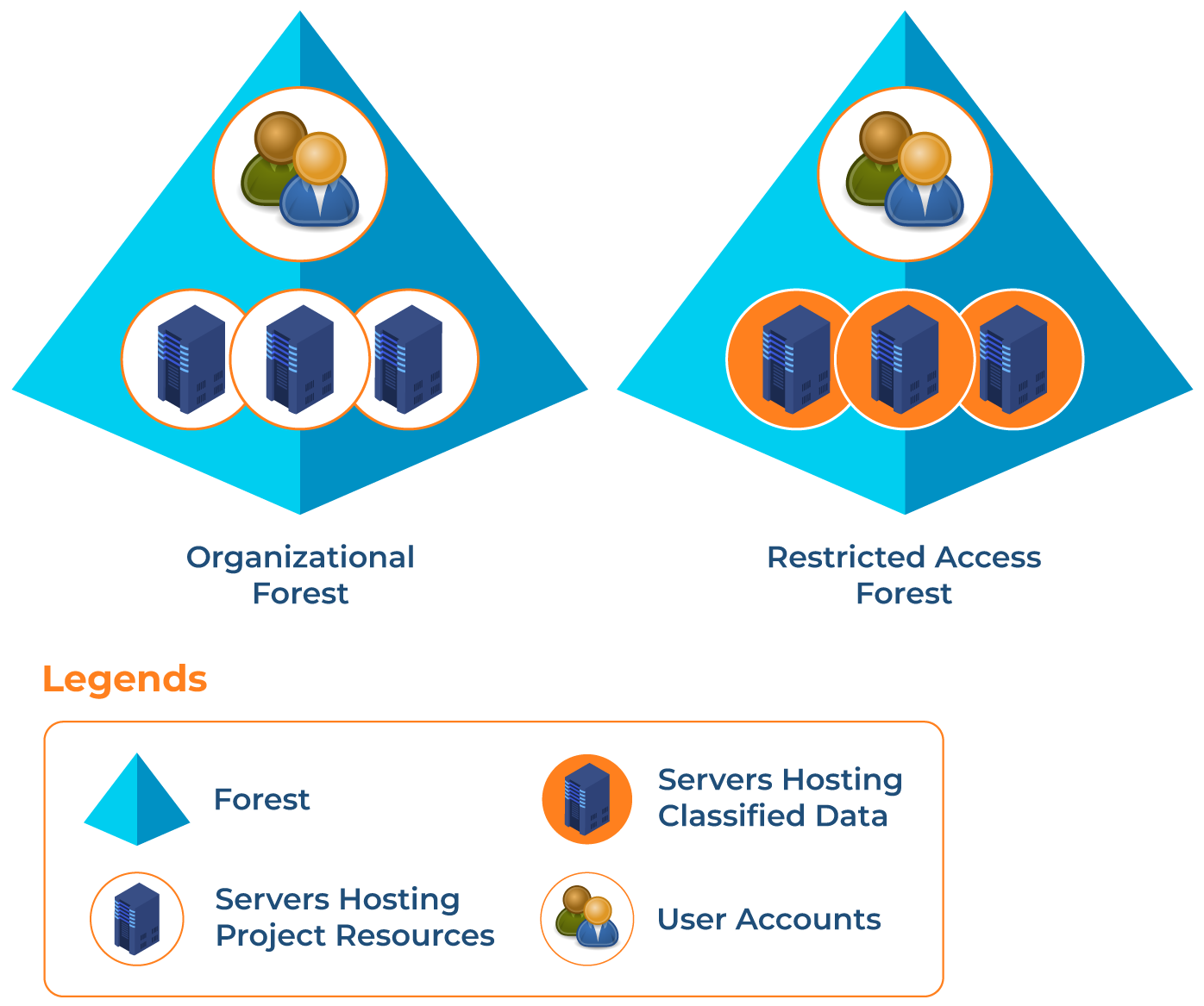
The restricted access forest model allows you to manage user accounts and resources in a forest that is separate from the rest of the organization. Users from other forests are unable to access restricted resources due to the lack of trust relationship between them.
You can use the restricted access forest model for confidential projects where security is the top priority. A restricted access forest can be created on a distinct physical network to manage this securely.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, Office 365

Unified Console
Use a single tool to administer and secure AD, Azure AD, and Office 365

Track Threats
Monitor AD for unwanted changes – detect for security or critical functions

Instant Recovery
Recover global enterprise-wide Active Directory forests in minutes, not days
How to create an Active Directory forest
Microsoft introduced two methods for system administrators to create an AD forest in a Windows Server operating system (OS). The first method uses Server Manager with a graphical user interface (GUI), and the second method uses PowerShell commands. In our case, we’ll use Server Manager to create an AD forest using Windows Server 2022. It’s easy to configure, as it offers a GUI for installing and configuring your AD forest. If you’re an experienced system administrator with some experience with PowerShell, you can also install and configure your AD forest using PowerShell commands.
You can create an AD forest in Windows Server 2022 using the following steps:
- Installing the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) server role.
- Promoting the server to a domain controller.
Prerequisites for Creating AD Forest in Windows Server 2022
The following are the prerequisites needed before creating an AD forest:
- A dedicated server: Dedicate a powerful machine with sufficient hardware resources to meet compute, memory, network, and storage requirements.
- Name the server: Change the default name of your domain controller according to your company’s naming conventions.
- Configure a static IP address for the Domain Controller (DC): Assign a static IP address to your server or domain controller.
Configuring AD Forest using Server Manager
We’ll assume you’ve already installed Windows Server 2022 and met the prerequisites. Let’s use the following steps to start configuring the AD forest.
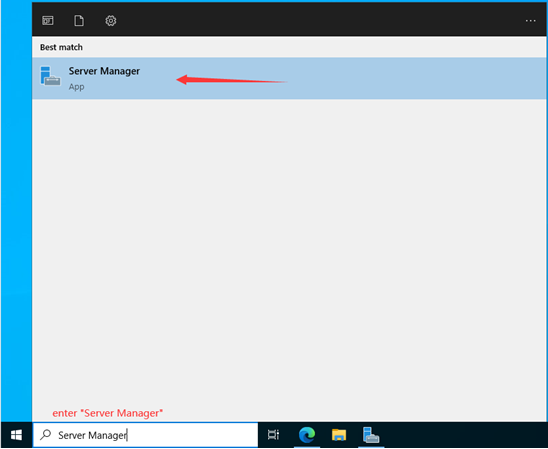
1. To install ADDS, open the Windows search box and type “Server Manager.” The Server Manager will open. It can be automatically launched when your Server 2022 restarts. You can open it from a search bar or wait for a few seconds to launch it automatically.
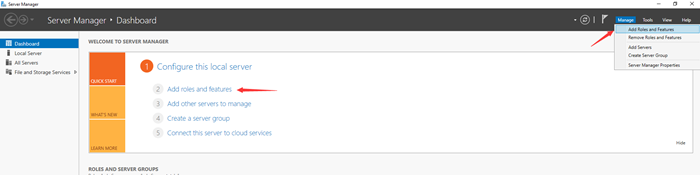
2. Click “Manage” in the top right corner and select “Add Roles and Features”. You can also click on it from the central pane of the Server Manager’s Dashboard.
It will open the wizard, and the “Before you begin” screen will appear. Click on “Next” to proceed.
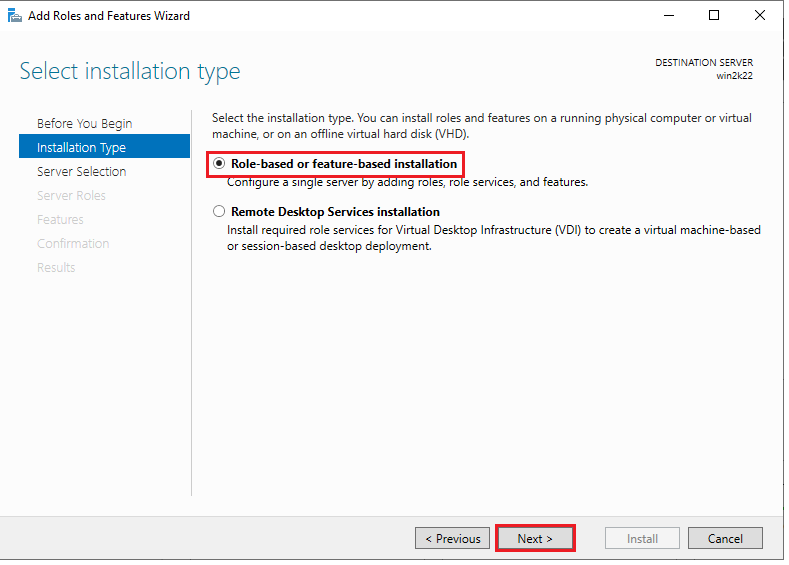
3. On the “Installation Type” screen, you’ll see two options. Choose the first option, “Role-based or feature-based installation.” This will configure a single server by adding roles, role services, and features. Click “Next” to continue.
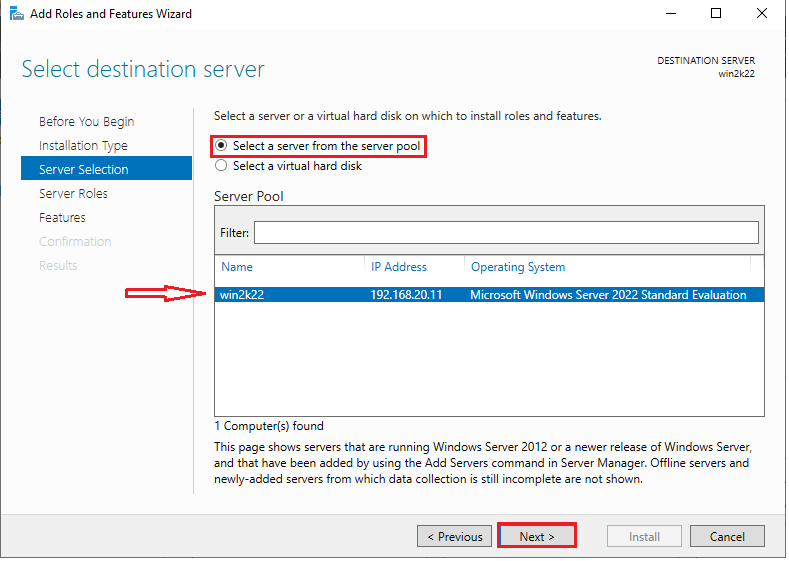
4. In the next window, select a server from the server pool and click “Next” to continue.
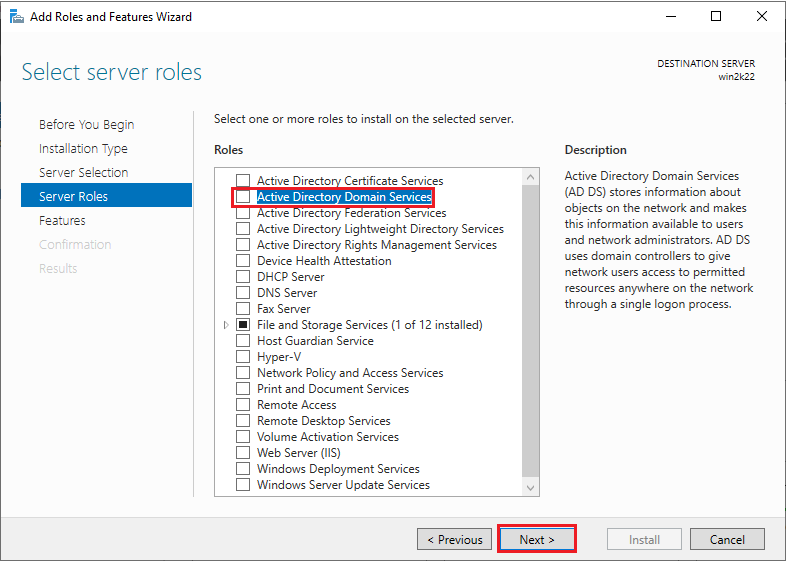
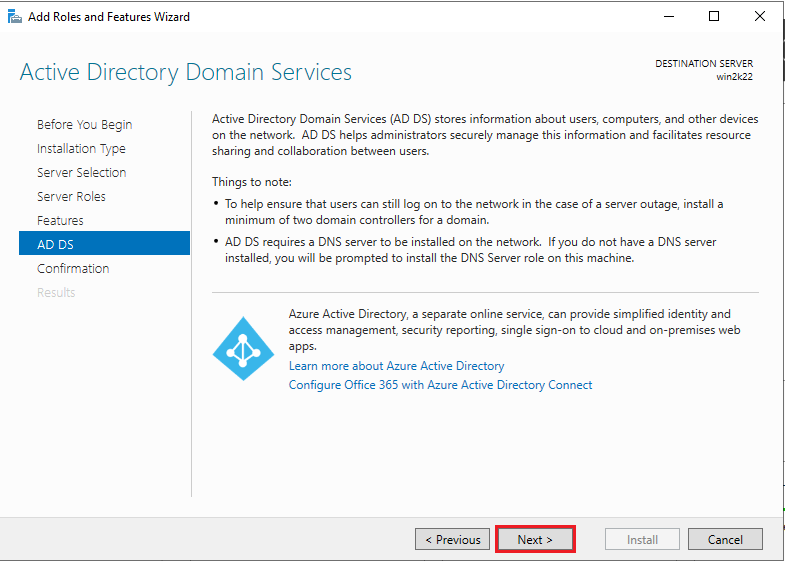
5. On the next screen, you’ll see several server roles. Choose “Active Directory Domain Services”.
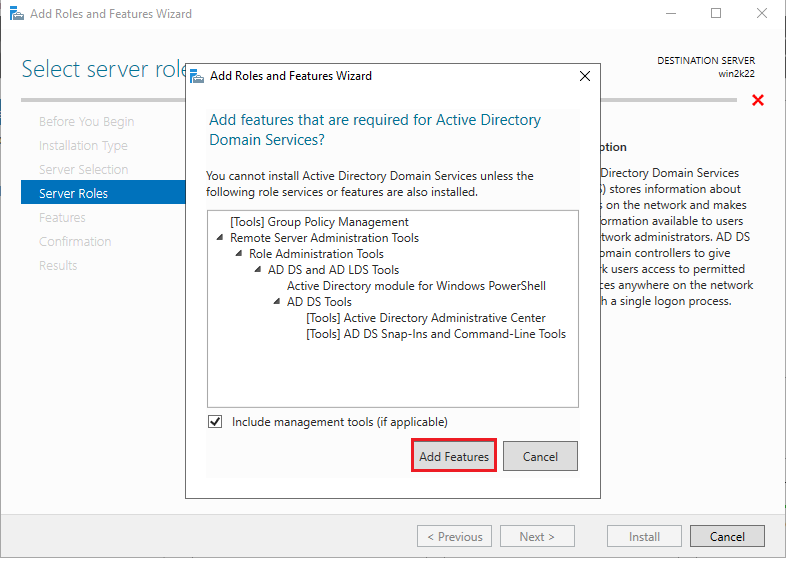
6. Once you click “Active Directory Domain Services”, you’ll be asked to add features in this window. Click the “Add Features” button to proceed, then click “Next” in the next window.
7. Review the ADDS settings and click “Next”.
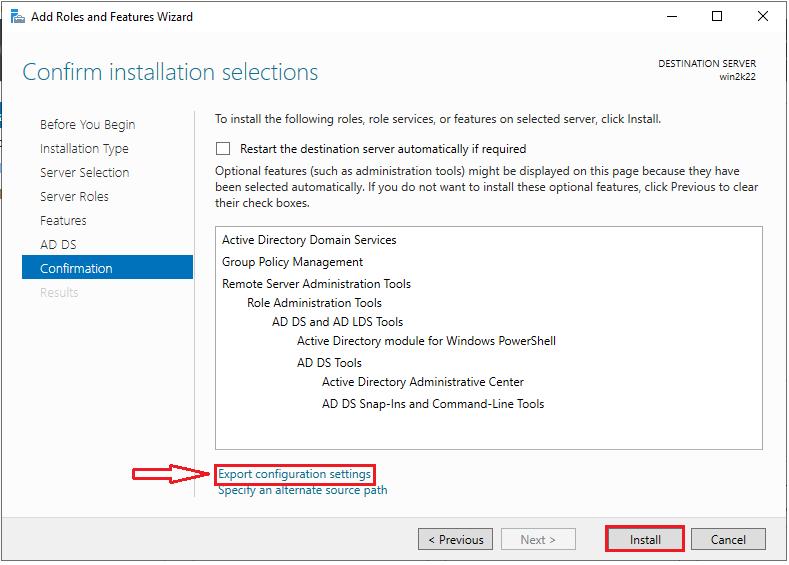
Note the information provided on the confirm installation selections page, and then click the “Install” button to begin the installation process.
If you want to use these configuration settings on another server, click the “Export configuration settings” link.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams
| Platform | Admin Features | Single Console for Hybrid (On-prem AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams) | Change Monitoring & Auditing | User Governance (Roles, Rules, Automation) | Forest Recovery in Minutes |
| Microsoft AD Native Tools | ✓ | ||||
| Microsoft AD + Cayosoft | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
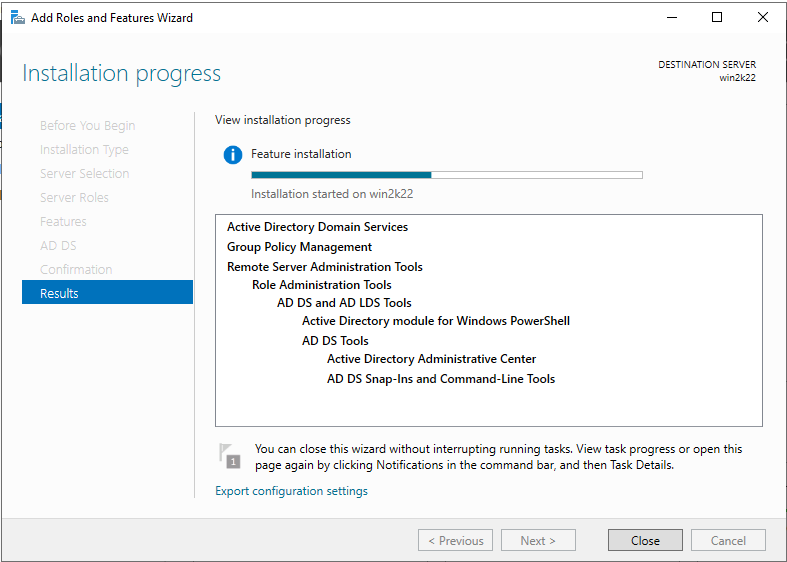
8. The ADDS installation process will start and will take some time. Once the installation is done, click “Close”.
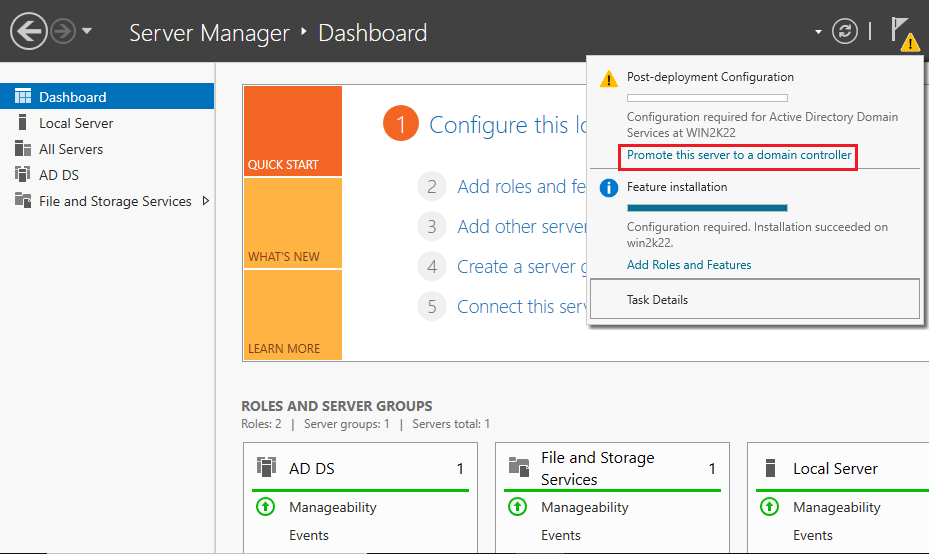
9. After installing ADDS binaries, you can promote the server to the Domain Controller (DC). To do this, open Server Manager > Yellow Flag Icon > Promote this server to the domain controller.
Watch a demo video of Cayosoft’s hybrid user provisioning
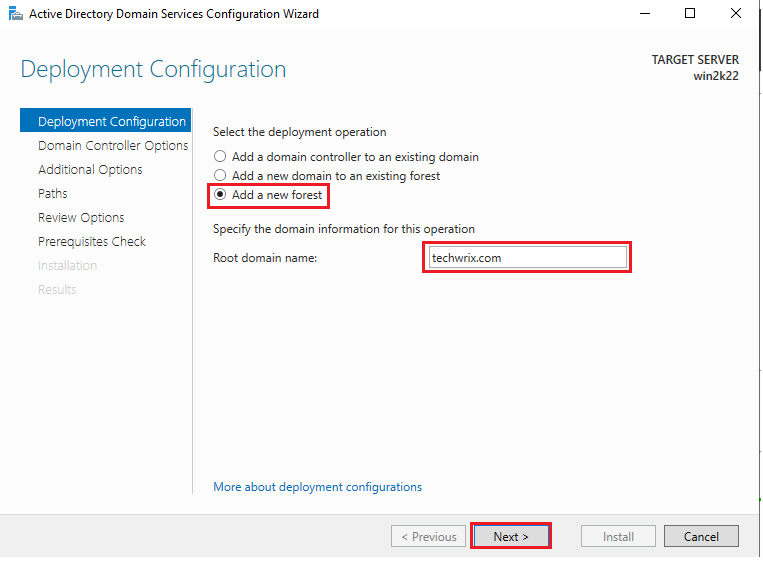
10. In the next window, we’ll add a new forest. Choose “Add a new forest” from the three options available, add a root domain name of your choice, and click “Next” to continue.
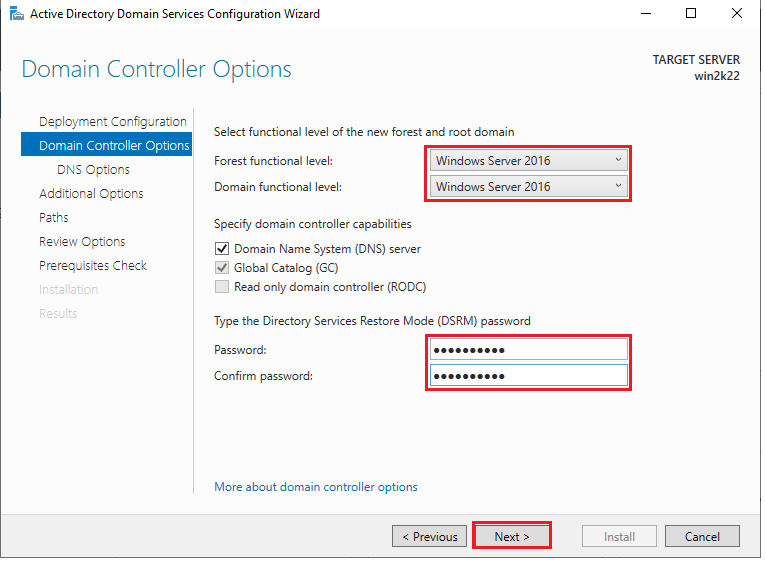
On the domain controller options page, you have several choices to make. The forest functional level determines which forest-level features are available and defines the minimum domain functional level for domains in your forest. Choosing Windows Server 2016 at this level means the minimum domain level is also Windows Server 2016.
The domain functional level determines the domain-level features available in this domain. We’ll keep Windows Server 2016 for both forest and domain functional levels.
DNS provides name resolution and is a critical service for ADDS. This installs the DNS server role on this server. This option is selected by default when first installing ADDS because DNS is required for Active Directory.
Global catalog servers provide forest-wide services. This option is not available but is selected when installing the first domain controller on the root domain because this server must be a global catalog server.
The read-only domain controller (RODC) option determines whether this domain controller is a read-only domain controller. This option is unavailable because the first domain controller cannot be a RODC.
11. Choose Windows Server 2016 your “Forest functional level”, and “Domain functional level”, set the “Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM)” password, confirm the password, and click “Next”.
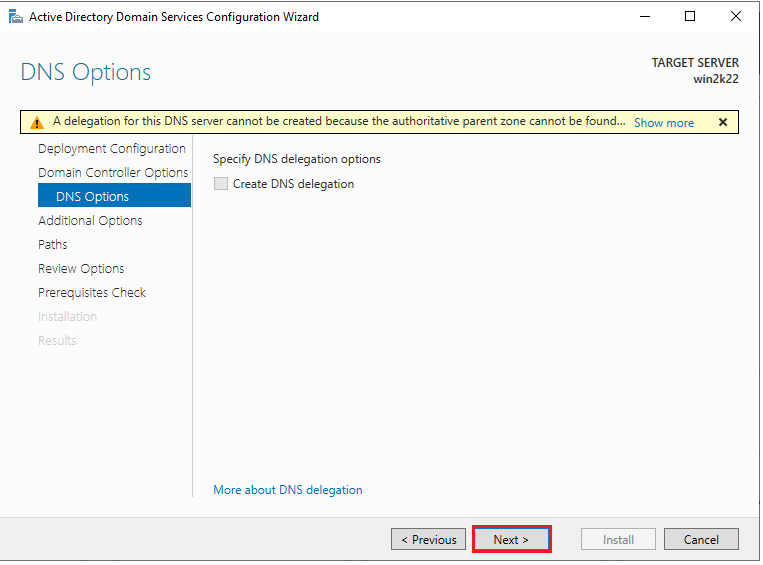
12. On the DNS Options window, leave everything as default and click “Next”.
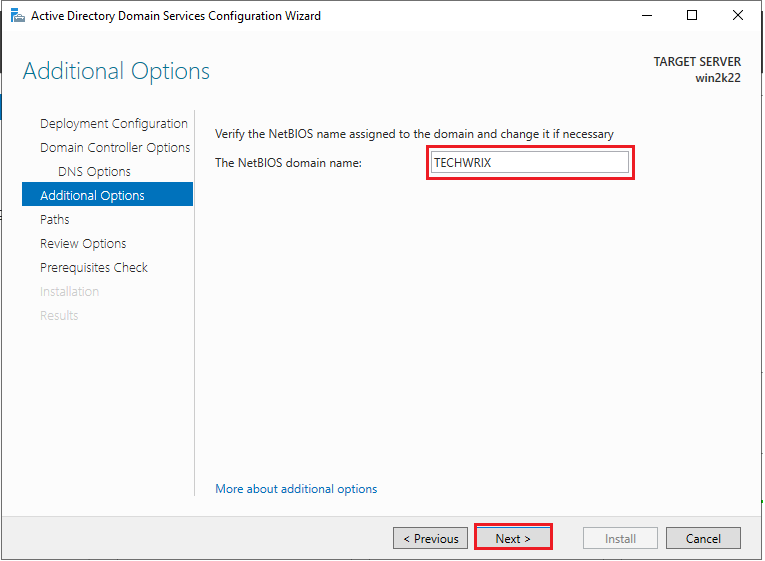
13. Enter “The NETBIOS domain name” and click “Next”.
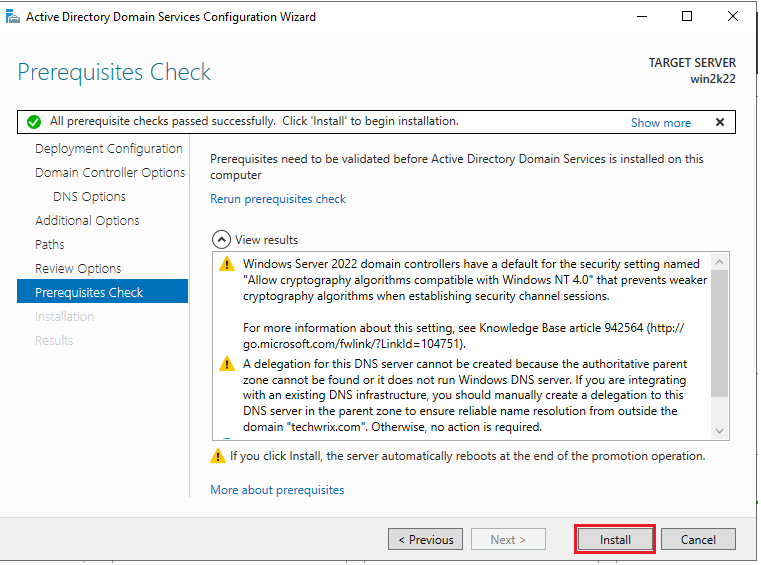
14. Set the desired installation path on the next window or leave it as the default. Review the configurations, check prerequisites, and click the “Install” button to proceed.
The installation process will begin. Once it is done, reboot the server, and you’ll be all set.
Six essential Active Directory forest best practices
The six best practices below can help you optimize your AD forest deployments.
Consolidate Active Directory forests where practical
Where necessary, try to consolidate your multiple forests into a single one. If you want to maintain security between two AD domains, you need to configure multiple forests in a single one, as each forest needs an additional management overhead. To connect multiple forests in Azure AD, all forests must reach a single Azure AD Connect sync server.
Patch and protect your AD environment
Install the latest security patches, implement strong authentication where required, and continuously monitor AD forests to avoid any unwanted situations. Also, regular audits should be conducted to identify any potential weaknesses.
Avoid Empty Forest Root Domain
Always try to avoid the Empty Forest Root Domain as it adds additional workload without any benefit, and Microsoft also discourages using it.
Plan for scalability and disaster recovery (DR)
Design your AD forest to easily scale with organizational requirements when needed. Also, develop a comprehensive DR plan including failover procedures, data restoration, and critical access to critical resources.
Maintain and optimization your AD environment
Take regular AD backups, clean up old accounts and groups, and monitor domain controllers to improve performance.
Track permissions and resources
System administrators should exercise great care when assigning permissions to users and groups. Permissions must be assigned according to roles and job responsibilities and regularly tracked and monitored.
How can Cayosoft help manage, monitor, and protect your AD Environment?
Cayosoft offers comprehensive solutions for managing, monitoring, and recovering your AD, Azure AD, and Microsoft 365 environments, including on-prem and the cloud. It enables hybrid management and protection, which assists organizations and businesses in increasing performance, improving security, and maintaining compliance. Cayosoft offers the following solutions:
Cayosoft Administrator
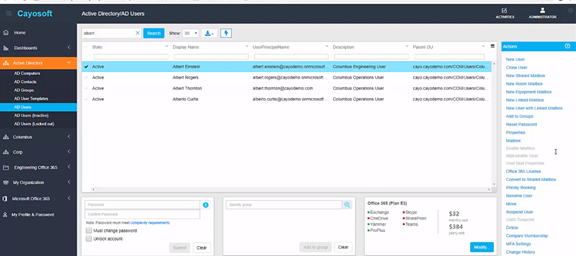
Cayosoft Administrator enables you to manage AD and Microsoft 365 for on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments using a single interface. It automates tasks, groups, and policy deployments. When you deploy it with your AD environment, it’ll provide you with efficiency, governance, and security over your systems administrators, users, and supporting staff.
It also delegates administrative tasks to other non-administrators, such as help desk technicians, departmental administrators, and end-users, if required. With Cayosoft Administrator, native privileges can be eliminated and delegated completely.
Cayosoft Guardian
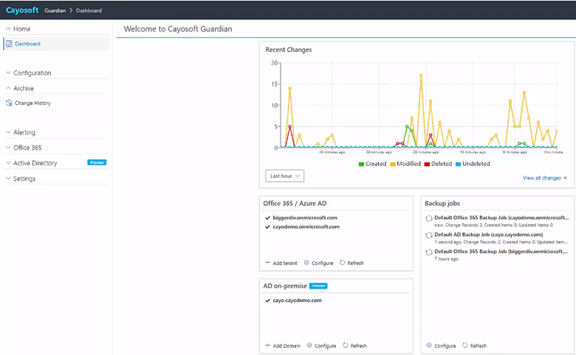
Cayosoft Guardian monitors, backs up, and recovers your important AD objects and attributes for AD security, such as users and groups. It also provides real-time alerts and monitoring in hybrid AD environments.
With Cayosoft Guardian, you can capture real-time change events with relevant information so they can be rolled back online without needing a backup. For Azure and Entra ID, Cayosoft Guardian allows you to roll back changes for most objects that bypass and cycle out of the recycle bin. Cayosoft Guardian is the only vendor to offer these features currently.
Guardian Forest Recovery
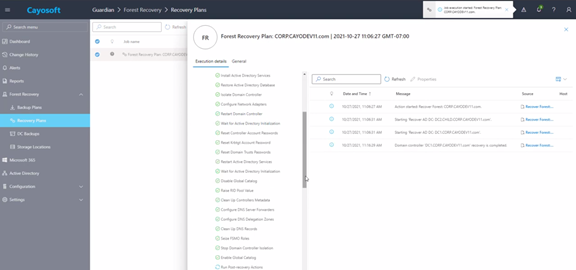
Guardian Forest Recovery accelerates backup and recovery by taking smaller backups and processing only the required data, which is important for AD forest recovery. It’s an instant recovery solution that allows you to recover AD on-premises, Azure AD, and hybrid AD.
Guardian Forest Recovery creates backups with only AD components to ensure no malware, virus, or OS-level corruption is introduced during the recovery process. It also offers a patented method of AD forest recovery that re-establishes the healthy and production-ready forest in a few minutes. In addition, Guardian Forest Recovery offers a partial AD recovery such as containers, OUs, DCs, etc. It offers continuous change monitoring, which enables rapid detection of harmful changes and prevents outages before they occur in the system.
Learn why U.S. State’s Department of Information Technology (DOIT) chose Cayosoft
Conclusion
Active Directory, whether on-premises or in the cloud, offers authentication and authorization capabilities to protect your data and systems. It is crucial to design, implement, monitor, and protect your Active Directory forests using the principles and practices we’ve discussed in this article.
To optimize their operations, teams should avoid the cumbersome nature of manually managing and monitoring AD attributes and objects. Cayosoft offers a comprehensive solution that helps you manage, monitor, and recover your AD environments on-premises and in the cloud effectively and efficiently.
To know more about how Cayosoft can help with hassle-free management and protection of your hybrid AD environments, request a free demo here.
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content